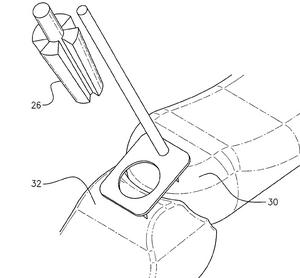
Los Angeles, CA – A copyright infringement, trademark infringement, Lanham Act unfair competition, and section 17200 complaint was filed in United States District Court, Los Angeles, by Hong Kong based Funrise Toys, Inc. over sales of allegedly infringing toys by defendants doing business as Aahs stores. Funrise Toys has federally registered trademarks for its “Gazillion Bubbles” word mark, bottle design trade dress, wand design trade dress, and machine design trade dress. Funrise Toys also claims to have trade dress and copyrights in the box packaging, in addition to the wand, machine, and bottle, for which it has received several copyright registration certificates. Funrise Toys also asserts that it has registered trademark rights in the green and purple colors used in the toys.
 The complaint alleges that the Aahs defendants manufacture and sell bubble machines which are substantially copied from the plaintiff’s “Gazillion Bubble Machine and box packaging and Defendants Aahs’ bubble bottle and wand is substantially copied from and contains the same physical appearance and features as the trade dress of” Plaintiff’s products or is a reproduction, counterfeit, copy, or colorable imitation thereof. Plaintiff further alleges that that defendants’ infringing product “is likely to, was intended to, and did cause confusion or mistake or to deceive the relevant trade and the public into believing that the” infringing product is “sponsored by, authorized by, associated with, originates from, and/or is in some way connected with or licensed by Plaintiff.” Plaintiff continues that the infringement was willful and intentional to trade upon plaintiff’s goodwill and reputation and asks for enhanced damages and attorneys’ fees. Plaintiff also asserts causes of action for Lanham Act unfair competition Section 43(a), and unfair competition under California Business and Professions Code § 17200. The case is titled: Funrise, Inc. v. Bhasin Enterprises, Inc., CV08-01117 DSF (C.D. California February 20, 2008).
The complaint alleges that the Aahs defendants manufacture and sell bubble machines which are substantially copied from the plaintiff’s “Gazillion Bubble Machine and box packaging and Defendants Aahs’ bubble bottle and wand is substantially copied from and contains the same physical appearance and features as the trade dress of” Plaintiff’s products or is a reproduction, counterfeit, copy, or colorable imitation thereof. Plaintiff further alleges that that defendants’ infringing product “is likely to, was intended to, and did cause confusion or mistake or to deceive the relevant trade and the public into believing that the” infringing product is “sponsored by, authorized by, associated with, originates from, and/or is in some way connected with or licensed by Plaintiff.” Plaintiff continues that the infringement was willful and intentional to trade upon plaintiff’s goodwill and reputation and asks for enhanced damages and attorneys’ fees. Plaintiff also asserts causes of action for Lanham Act unfair competition Section 43(a), and unfair competition under California Business and Professions Code § 17200. The case is titled: Funrise, Inc. v. Bhasin Enterprises, Inc., CV08-01117 DSF (C.D. California February 20, 2008).
 Los Angeles Intellectual Property Trademark Attorney Blog
Los Angeles Intellectual Property Trademark Attorney Blog


 Tom Gramatis was one of the original defendants in the 2002 lawsuit and settlement agreement and he has recently built two additional buildings with rooftop seating. The Cubs allege that Gramatis breached their settlement agreement by not paying the agreed upon royalties and has not paid any royalties for the new buildings. Interestingly, the Cubs have dropped their dubious copyright infringement claim from this lawsuit – undoubtedly a lesson learned from 2002 – and only assert that Gramatis is infringing on the Cubs’ trademarks and falsely advertising an association with the team in his promotional material and website. The Cubs allege that “Defendants’ marketing efforts are, and have been, likely to cause confusion, to cause mistake or to deceive as to, inter alia, the affiliation, association or connection between Defendants and the Cubs and the Cubs’ approval or sponsorship of Defendants’ business activities.”
Tom Gramatis was one of the original defendants in the 2002 lawsuit and settlement agreement and he has recently built two additional buildings with rooftop seating. The Cubs allege that Gramatis breached their settlement agreement by not paying the agreed upon royalties and has not paid any royalties for the new buildings. Interestingly, the Cubs have dropped their dubious copyright infringement claim from this lawsuit – undoubtedly a lesson learned from 2002 – and only assert that Gramatis is infringing on the Cubs’ trademarks and falsely advertising an association with the team in his promotional material and website. The Cubs allege that “Defendants’ marketing efforts are, and have been, likely to cause confusion, to cause mistake or to deceive as to, inter alia, the affiliation, association or connection between Defendants and the Cubs and the Cubs’ approval or sponsorship of Defendants’ business activities.”  The defendants, Soft Air USA, Inc. and a subsidiary of Sports Authority, are accused of copying and selling toy helicopters that infringe on Plaintiffs’ Air Hogs® Havoc Heli™ Helicopter’s patents and copyrights. Plaintiffs allege that Defendants’ helicopters are identical to the Air Hogs® Havoc Heli™ Helicopter that “Defendants’ knock off helicopters were recently recalled after an investigation by the Consumer Product Safety Commission in response to consumer complaints that the rechargeable battery packs were catching fire.” Plaintiffs continue that they were “bombarded with calls from customers who mistakenly believed that Defendants’ inferior and dangerous knock off product was made by Silverlit.” Plaintiffs allege that customers believed that the Defendants’ voluntarily recall included the Air Hogs® Havoc Heli™ Helicopter and returned the genuine product to Plaintiffs. The case is styled as: Silverlit Toys Manufactoy, LTD v. Soft Air USA, Inc., CV08-01053 JFW (C.D. California).
The defendants, Soft Air USA, Inc. and a subsidiary of Sports Authority, are accused of copying and selling toy helicopters that infringe on Plaintiffs’ Air Hogs® Havoc Heli™ Helicopter’s patents and copyrights. Plaintiffs allege that Defendants’ helicopters are identical to the Air Hogs® Havoc Heli™ Helicopter that “Defendants’ knock off helicopters were recently recalled after an investigation by the Consumer Product Safety Commission in response to consumer complaints that the rechargeable battery packs were catching fire.” Plaintiffs continue that they were “bombarded with calls from customers who mistakenly believed that Defendants’ inferior and dangerous knock off product was made by Silverlit.” Plaintiffs allege that customers believed that the Defendants’ voluntarily recall included the Air Hogs® Havoc Heli™ Helicopter and returned the genuine product to Plaintiffs. The case is styled as: Silverlit Toys Manufactoy, LTD v. Soft Air USA, Inc., CV08-01053 JFW (C.D. California). Chanel alleges that Defendants are “promoting, and or otherwise advertising, distributing, selling, and/or offering for sale counterfeit products, including at least necklaces and costume jewelry bearing trademarks which are exact copies of Chanel Marks” and are counterfeit, lower quality goods that also incorporate Chanel’s trade dress. The complaint further alleges that the “net effect of Defendants’ actions is to confuse consumers who will believe Defendants’ Counterfeit Goods are genuine goods originating from and approved by Chanel.” In addition to preliminary and permanent injunctive relief, Chanel seeks three times its actual damages under 15 U.S.C. § 1117, or, at its election, seeks statutory damages of $1,000,000.00 (one million dollars) from each defendant under 15 U.S.C. § 1117(c)(2) of the Lanham Act. The case is styled as Chanel, Inc. v. Kin Fung Poon et al., EDCV08-0224 VAP (CD CA 2008).
Chanel alleges that Defendants are “promoting, and or otherwise advertising, distributing, selling, and/or offering for sale counterfeit products, including at least necklaces and costume jewelry bearing trademarks which are exact copies of Chanel Marks” and are counterfeit, lower quality goods that also incorporate Chanel’s trade dress. The complaint further alleges that the “net effect of Defendants’ actions is to confuse consumers who will believe Defendants’ Counterfeit Goods are genuine goods originating from and approved by Chanel.” In addition to preliminary and permanent injunctive relief, Chanel seeks three times its actual damages under 15 U.S.C. § 1117, or, at its election, seeks statutory damages of $1,000,000.00 (one million dollars) from each defendant under 15 U.S.C. § 1117(c)(2) of the Lanham Act. The case is styled as Chanel, Inc. v. Kin Fung Poon et al., EDCV08-0224 VAP (CD CA 2008).